MultiplayerSynchronizer: A Complete Informative Guide for Developers and Gamers
In modern online gaming and real-time applications, smooth multiplayer synchronization is no longer optional—it is essential. One term that frequently appears in developer discussions, game engine documentation, and networking tutorials is MultiplayerSynchronizer. Whether you are a game developer, modder, or tech enthusiast, understanding how MultiplayerSynchronizer works can dramatically improve performance, stability, and player experience.
This article provides a clear, SEO-optimized, and fully informative breakdown of MultiplayerSynchronizer, explaining what it is, how it works, and why it matters in today’s multiplayer ecosystem.
What Is MultiplayerSynchronizer?
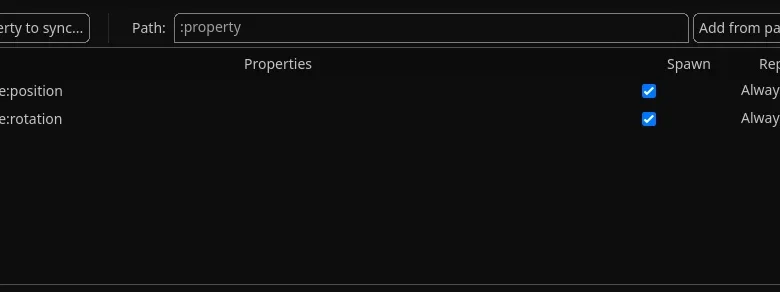
MultiplayerSynchronizer is a networking component or system designed to keep game states consistent across multiple players in a multiplayer environment. Its primary role is to ensure that positions, actions, animations, variables, and events remain synchronized between all connected clients and the server.
In simpler terms, MultiplayerSynchronizer makes sure that:
-
What Player A sees
-
Matches what Player B sees
-
And aligns with what the server authoritatively controls
Without proper synchronization, players experience lag, desync, rubber-banding, or inconsistent gameplay, which can ruin immersion and fairness.
How MultiplayerSynchronizer Works
At its core, MultiplayerSynchronizer operates by tracking changes in game objects and transmitting those changes over the network. It commonly uses:
-
State replication
-
Authority rules
-
Network ticks or frames
-
Delta compression
Instead of sending complete data every time, the system often sends only what has changed, reducing bandwidth usage. Synchronization can be:
-
Server-authoritative (most secure)
-
Client-authoritative (faster but less secure)
-
Hybrid (balanced approach)
The synchronizer ensures that updates occur in the correct order and timing, preventing visual or logical mismatches between players.
Key Features of MultiplayerSynchronizer
A well-designed MultiplayerSynchronizer includes several critical features that support stable multiplayer gameplay:
-
Automatic variable replication
-
Transform synchronization (position, rotation, scale)
-
Event syncing (animations, triggers, actions)
-
Interpolation and extrapolation for smooth movement
-
Lag compensation techniques
These features allow developers to focus on gameplay logic instead of constantly writing custom network code. For players, this results in responsive controls and fair interactions, even in fast-paced games.
Why MultiplayerSynchronizer Is Important in Online Games
Multiplayer games live or die based on network quality. MultiplayerSynchronizer plays a central role in:
-
Preventing cheating
-
Maintaining fairness
-
Ensuring consistency
-
Improving player trust
In competitive games, even a slight desynchronization can lead to unfair advantages. In cooperative games, poor syncing can break immersion or cause mission failures. That’s why nearly all modern multiplayer engines rely on some form of synchronization framework.
Without MultiplayerSynchronizer systems, developers would need to manually manage every network update, dramatically increasing complexity and bugs.
Common Use Cases of MultiplayerSynchronizer
MultiplayerSynchronizer is not limited to one genre or platform. It is widely used in:
-
Online multiplayer games (FPS, RPG, MMO, survival)
-
Co-op and peer-to-peer games
-
Simulation and training software
-
Multiplayer VR and AR experiences
-
Real-time collaborative applications
From syncing player movement in a shooter to updating shared environments in a sandbox game, MultiplayerSynchronizer ensures everyone experiences the same reality.
Performance Optimization and Best Practices
While powerful, MultiplayerSynchronizer must be used correctly to avoid performance issues. Best practices include:
-
Sync only necessary variables
-
Reduce update frequency when possible
-
Use interpolation instead of raw position updates
-
Separate visual sync from game logic
-
Monitor bandwidth usage
Optimized synchronization leads to lower latency, fewer packet drops, and smoother gameplay, especially for players on slower connections.
Future of Multiplayer Synchronization Technology
As multiplayer gaming continues to evolve, MultiplayerSynchronizer systems are becoming more advanced. Emerging trends include:
-
Rollback networking
-
Prediction-based synchronization
-
Cloud-hosted authoritative servers
-
AI-assisted network optimization
With cross-platform play and massive online worlds becoming standard, synchronization technology will remain one of the most critical pillars of game development.
Conclusion
MultiplayerSynchronizer is the backbone of modern multiplayer experiences. It ensures that players stay connected not just through servers, but through shared, consistent gameplay reality. Whether you are building a competitive shooter, a cooperative adventure, or a real-time application, understanding and implementing proper synchronization is essential for success.
As multiplayer demand grows, so does the importance of reliable, optimized synchronization systems—and MultiplayerSynchronizer stands at the center of it all.
FAQs
1. Is MultiplayerSynchronizer a specific tool or a general concept?
It can refer to both a specific engine component and a general synchronization system.
2. Does MultiplayerSynchronizer reduce lag?
It helps manage and mask latency, but cannot eliminate lag entirely.
3. Is server authority better than client authority?
Yes, server authority is more secure and fair, especially for competitive games.
4. Can MultiplayerSynchronizer prevent cheating?
It significantly reduces cheating opportunities when properly configured.
5. Is MultiplayerSynchronizer required for small multiplayer games?
Yes, even small games benefit from basic synchronization systems.