Master Multiplayer Networking with multiplayersynchronizer: Build Seamless Real-Time Game Sync
Create powerful multiplayer experiences by mastering multiplayersynchronizer. Build consistent game worlds, reduce desynchronization errors, and ensure every connected player sees the same state in real time. Follow this guide step by step and implement synchronization the right way.
Understand the Core Purpose of multiplayersynchronizer
Start by understanding what multiplayersynchronizer actually does. Use it to synchronize properties of game objects across multiple connected peers. Ensure that when one player moves, jumps, or changes state, every other player sees the same result instantly.
Focus on state replication. Synchronize position, rotation, animations, health values, and other gameplay variables. Avoid manually writing repetitive network update code. Instead, let the synchronizer handle automatic property updates between the authority (usually the server or host) and connected clients.
Recognize that synchronization works best when you clearly define which peer has authority. Assign authority properly. Allow only the authoritative instance to push updates. Prevent conflicting updates from multiple peers. Maintain control and consistency at all times.
Commit to understanding network roles before implementation. Decide whether your game runs on a server-authoritative model or a peer-to-peer structure. Design your synchronization logic accordingly.
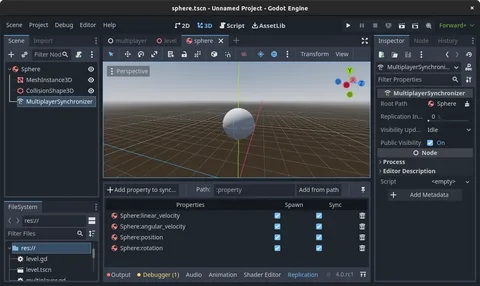
Configure multiplayerSynchronizer Correctly in Your Scene
Add the multiplayersynchronizer node to the objects you want to replicate. Attach it directly to the player character, NPC, or interactive object that requires synchronization.
Define the properties to replicate carefully. Select only what you truly need. Synchronize essential gameplay variables like:
- Transform (position and rotation)
- Health values
- Animation states
- Action flags (jumping, attacking, interacting)
Avoid syncing unnecessary data. Reduce bandwidth usage. Improve performance. Keep your network efficient.
Match node paths exactly across all clients. Ensure identical scene structures. Prevent silent failures caused by mismatched node hierarchies. Test synchronization across multiple devices to confirm consistency.
Enable and configure visibility rules. Control which peers receive updates. Reduce traffic by syncing objects only when relevant. For example, synchronize enemy data only for players within a certain range.
Establish Strong Authority and Ownership Rules
Assign multiplayer authority clearly. Set ownership of player characters to the corresponding connected peer. Allow the server to retain control over critical gameplay logic.
Prevent desynchronization by enforcing a single source of truth. Do not allow multiple peers to overwrite the same property simultaneously. Use authority-based synchronization to maintain stability.
Implement these best practices:
-
Assign authority during player spawn.
-
Restrict property modification to the authority.
-
Validate changes server-side before replication.
-
Combine synchronizer logic with secure validation checks.
Strengthen your architecture by separating client prediction from server validation. Allow smooth movement locally but confirm final positions through authoritative synchronization. Balance responsiveness with fairness.
Optimize Performance and Network Efficiency
Reduce network load. Optimize synchronization frequency. Do not blindly sync every frame unless necessary.
Control update rates strategically. Synchronize high-priority properties more frequently than low-priority ones. For example:
- Sync player movement frequently.
- Sync cosmetic properties less often.
- Avoid syncing static objects entirely.
Compress data when possible. Avoid large structures. Use lightweight variables. Improve performance especially in games with many simultaneous players.
Test your implementation under stress conditions. Simulate multiple connections. Monitor bandwidth usage. Identify bottlenecks early. Fix inefficient property replication before scaling your project.
Disable synchronization when objects are inactive. Stop syncing entities that are destroyed, hidden, or outside gameplay relevance. Save processing power and network traffic.
Combine multiplayerSynchronizer with RPCs for Advanced Behavior
Do not rely solely on multiplayersynchronizer for every networking need. Combine it with Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) for complex gameplay events.
Use synchronization for continuous property updates. Use RPCs for discrete events such as:
- Triggering abilities
- Playing sound effects
- Spawning projectiles
- Executing scripted interactions
Design a hybrid networking model. Let the synchronizer handle state replication while RPCs handle gameplay commands. Maintain clarity between state updates and action triggers.
Validate RPC calls carefully. Prevent cheating by confirming actions on the server before applying changes. Strengthen security and protect competitive gameplay integrity.
Test edge cases thoroughly. Disconnect clients during gameplay. Reconnect them. Ensure proper state resynchronization. Handle packet loss gracefully.
Troubleshoot Common Synchronization Problems
Identify synchronization issues quickly. Watch for these common problems:
Fix Desynchronization Errors
Check authority assignments first. Confirm that only the correct peer modifies synchronized properties. Inspect your scene structure. Ensure consistent node naming.
Resolve Physics Conflicts
Avoid directly overriding physics bodies without caution. Apply position corrections within physics processing callbacks. Prevent jittering or snapping behavior.
Prevent Peer Isolation
Ensure that synchronization reaches all peers, not just the host. Verify relay settings if necessary. Confirm that updates propagate across the full network.
Debug Visibility Settings
Review visibility filters. Confirm that objects are not unintentionally hidden from certain peers. Adjust visibility configurations carefully.
Build Scalable Multiplayer Systems with Confidence
Design your multiplayer architecture for growth. Plan for increasing player counts. Structure synchronization logic modularly.
Follow these strategic steps:
- Create reusable player templates with built-in synchronization.
- Develop standardized authority assignment methods.
- Document synchronization rules clearly.
- Implement automated testing for multiplayer sessions.
Monitor gameplay consistency regularly. Compare client states during development. Detect mismatches early.
Keep user experience in focus. Reduce latency where possible. Maintain smooth animations. Ensure reliable state updates even under unstable network conditions.
Apply Practical Implementation Strategies
Implement multiplayersynchronizer thoughtfully. Begin with a small prototype. Synchronize only player movement first. Expand gradually to health, animations, and environment objects.
Follow this development roadmap:
- Prototype basic movement sync.
- Add health synchronization.
- Introduce animation state replication.
- Integrate event-driven RPC actions.
- Stress-test with multiple clients.
- Optimize bandwidth and performance.
Document every synchronization decision. Maintain clean and readable networking code. Improve maintainability and debugging efficiency.
Stay updated with engine documentation and networking best practices. Review official resources regularly to refine your approach and ensure compatibility with the latest engine versions.
Strengthen Security and Maintain Fair Play
Protect your multiplayer system from exploitation. Never trust client data blindly. Validate important gameplay actions on the server.
Implement server-side checks for:
- Movement speed limits
- Health modification
- Damage calculations
- Item usage
Use synchronization as a replication tool, not a validation mechanism. Separate authority from trust. Preserve fairness and prevent cheating.
Conclusion
Master multiplayersynchronizer by implementing it with precision, authority control, and optimization strategies. Synchronize essential properties. Reduce unnecessary data replication. Combine synchronization with RPCs. Validate actions server-side. Test thoroughly under real-world conditions.
Build scalable systems. Maintain performance efficiency. Protect gameplay integrity. Deliver smooth, synchronized multiplayer experiences that feel seamless and professional.



